SSH For Your IoT Devices And Router: Keeping Things Safe And Connected
Have you ever wondered how to truly keep your smart home gadgets or even your internet router safe from prying eyes? It's a question many folks ask, especially as we bring more and more connected things into our living spaces. You might have a bunch of smart bulbs, security cameras, or even a specialized server like one running Elastix, all linked up to your home network. So, making sure these devices communicate securely is, you know, a pretty big deal.
Think about all the data flowing back and forth from your IoT devices. Whether it's video from a camera or just status updates from a smart plug, you want that information to stay private. This is where something called SSH, or Secure Shell, comes into play. It's a way to create a protected tunnel for your commands and data, keeping everything nice and private as it moves across your network, or even the wider internet.
Using SSH with your IoT devices and router gives you a powerful way to manage them remotely and securely. It's about having that peace of mind, knowing that when you check on your devices, you're doing it in a way that helps prevent unauthorized access. This article will walk you through why SSH matters for your connected home and how you can get it working for you, addressing some common hiccups along the way, too it's almost a given that you'll run into a few things.
Table of Contents
- Why SSH for Your IoT Devices and Routers?
- Getting Started with SSH on Your Devices
- Common SSH Challenges and How to Handle Them
- Best Practices for SSH Security
- Frequently Asked Questions About SSH for IoT and Routers
- Conclusion
Why SSH for Your IoT Devices and Routers?
A Secure Connection for Your Connected Things
When you have smart devices, like those little gadgets that control your lights or monitor your home, they often need to be managed. You might want to update their software, change settings, or check on their status. Doing this over an unsecured connection is, well, a bit like shouting your private information across a crowded room. Anyone listening could pick it up. SSH, on the other hand, makes a private conversation possible.
It creates a protected channel, encrypting all the data that goes between your computer and your device. This means that even if someone were trying to snoop on your network, they wouldn't be able to make sense of what you're sending or receiving. It's a very good way to keep your commands and information safe, especially when dealing with things like router settings or sensitive IoT data. So, you know, it's pretty important.
Keeping Your Digital Home Safe
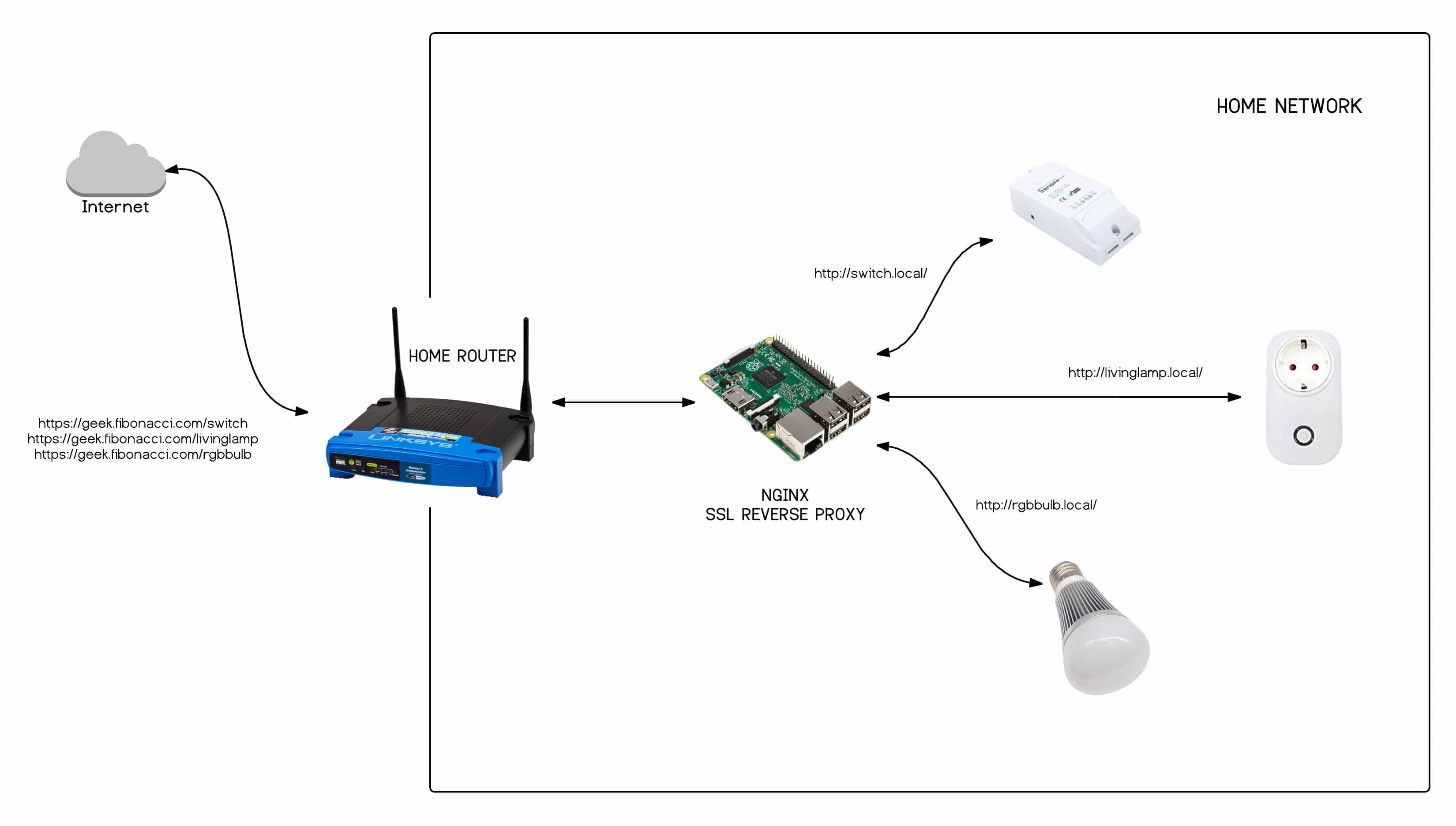
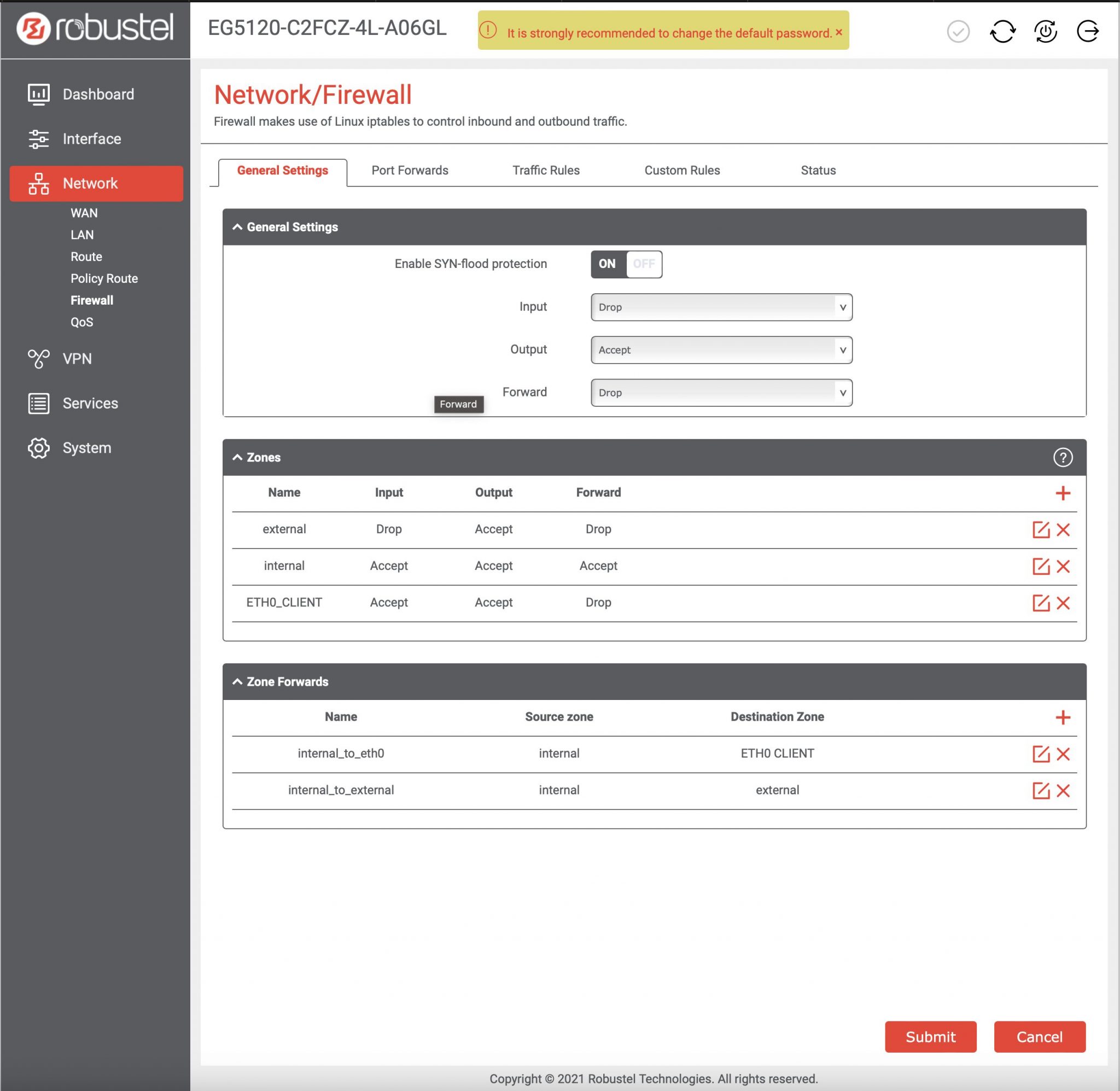
Your router is, in a way, the front door to your home network. If that door isn't secure, then all your connected devices could be at risk. Many routers offer SSH access, letting you manage them from a distance using a secure method. This is much better than using older, less safe ways to connect, which might leave your network open to problems. For instance, if you're running other services locally, like an Elastix server, you really want to make sure your network's entry points are buttoned up.
For IoT devices, SSH allows you to get to the "guts" of the device, if it supports it. This is great for custom setups or for fixing things if they go wrong. You can, for example, access a device to pull log files or run specific commands, all without worrying too much about someone intercepting your session. It helps you keep a tight grip on your digital home's security, which is something you definitely want, right?
Getting Started with SSH on Your Devices
Checking for SSH Access
Before you can use SSH, you need to know if your IoT device or router actually supports it. Many newer smart devices and most modern routers do, but sometimes it's turned off by default. You'll usually find an option to enable SSH in the device's web interface or its setup application. For a router, you might log in to its administrative page through your web browser and look for "Administration," "Security," or "Remote Access" settings. It's often tucked away in there somewhere, you know.
Once you think it's enabled, you can try to connect from your computer. If you're on a Mac or Linux machine, you'll use the terminal. It's very similar to how you might connect to a NAS from an OSX command line terminal, without needing much client setup. For Windows users, tools like PuTTY are pretty common for this. You just type `ssh username@device_ip_address` and see what happens. If it asks for a password, you're probably on the right track, that is.
Setting Up SSH Keys for Better Security
Using passwords with SSH is okay, but using SSH keys is a lot safer. Instead of typing a password, you use a special pair of digital keys: a public key that lives on the device you want to connect to, and a private key that stays safe on your computer. When you try to connect, the two keys talk to each other to confirm it's really you. This method is much harder for bad actors to crack.
You generate these keys on your computer. For example, after installing Git on a new work computer, you might generate an SSH key and add it to a service like GitLab. This is pretty much the same process. Sometimes, you might need to use a specific keypair for a connection, not just your default `id_rsa` key. This is handy if you're connecting to a special SSH proxy server that needs its own unique key. Your client remembers the host key associated with a particular server, so it knows who it's talking to, which is pretty neat.
Changing the Default SSH Port (like 5643)
By default, SSH usually uses port 22. While this is fine, many people like to change it to a different, less common port, like 5643. This doesn't make your connection inherently more secure, but it can help reduce the amount of automated "noise" from bots trying to guess passwords on the standard port. It's a bit like changing your front door from the street to a side alley; it's still a door, but fewer people might stumble upon it by chance.
If you're managing a server, perhaps one running Ubuntu Server, you can change the SSH port by editing its configuration. For instance, you might use a command like `systemctl edit ssh.socket` to adjust the listening port. After restarting the SSH service, you can then connect via the new port. This is a common practice for servers, and some advanced routers might let you do this too, so it's worth checking if your device allows it.
Common SSH Challenges and How to Handle Them
Connection Troubles: When SSH Just Won't Connect
It's pretty frustrating when SSH just doesn't work. Maybe it was working fine, and then suddenly it stopped. One common reason for this is a change in your system's configuration or a new service interfering. For example, if you installed something new, like GitLab, and then SSH stopped working, it's possible the new installation changed a network setting or even tried to use the same port. Before that install, SSH was probably correctly working, so that's a good clue.
Sometimes, client-side issues can pop up too. Someone mentioned meeting an issue after changing an Apple ID password and restarting their Mac, which then affected SSH. This suggests that updates or changes on your local machine can sometimes mess with how your SSH client handles keys or connections. It's a good idea to check your local SSH configuration files, usually found in the `.ssh` directory in your home folder. This directory isn't always created by default, but it's where your keys and settings live when you call `ssh somehost`.
Dealing with Host Key Warnings
When you connect to a new server or device using SSH for the first time, you'll usually get a warning about the host key. SSH tells you that every host has a unique key, and clients remember the host key associated with a particular server. This is a security measure to make sure you're connecting to the right device and not a fake one. If the key changes unexpectedly, SSH will warn you, because it thinks someone might be trying to trick you.
If you see a warning about a changed host key, and you know the device's setup has changed (maybe you reinstalled its operating system or got a new router), you might need to remove the old host key from your computer's `known_hosts` file. This file, usually in your `.ssh` directory, stores all those remembered keys. You can simply run a command to remove the old entry for that specific device, like taking a command from Git's suggestions for fixing repository issues. It's a quick fix that often solves the problem, you know.
Remote Access for Specific Needs (like Databases or GUIs)
SSH isn't just for command-line access; it can also forward other types of connections. For example, if you have PostgreSQL installed on a server and you can connect to it using `psql` when you SSH into the server directly, you might want to configure a graphical tool like pgAdmin III to do the remote connection through SSH. This is called SSH tunneling or port forwarding, and it's a really useful trick for securely accessing services that aren't meant to be exposed directly to the internet.
Similarly, if you want to access a graphical user interface (GUI) on a remote Ubuntu server from your workstation, SSH can help with X11 forwarding. If you run `ssh` and the display isn't set, it means X11 forwarding isn't happening. To confirm it's forwarding, you can check for a line containing "requesting X11 forwarding" in the output of your SSH connection. This can be a lightweight way to get GUI access over SSH, which is rather convenient for managing a server without a full remote desktop setup.
Automating Tasks with SSH
One of the really cool things about SSH is its ability to automate tasks. You can write scripts that connect to your IoT devices or router and run commands without you having to type them manually every time. For instance, if you're writing a script to automate some command line actions in Python, you might make calls like `cmd = "some unix command"` and then execute that over an SSH connection.
This is especially handy if you need to manage multiple devices or perform repetitive actions. You can even set up a bash script on one server to execute commands on another server via SSH, using your private key file for authentication. This means your script can log in and do its work without needing a password typed in. It makes managing a bunch of devices much, much simpler, honestly.
Best Practices for SSH Security
Always Use Key-Based Authentication
We talked about SSH keys before, and it bears repeating: always use key-based authentication instead of passwords whenever you can. Passwords, even strong ones, can be guessed or brute-forced over time. SSH keys, however, are nearly impossible to guess. They provide a much stronger form of security for your connections to IoT devices and routers. It's a simple change that makes a very big difference, you know.
Make sure your private keys are kept safe on your local machine. They should have very strict permissions so only you can read them. If you're using specific keypairs for different connections, perhaps for a proxy server as mentioned earlier, keep them organized and protected. The default location for keys is usually within your `~/.ssh` directory, like `~/.ssh/identity` for older protocol versions, so that's where you'd typically find them.
Keep Software Updated
This might sound obvious, but it's super important to keep the software on your IoT devices, router, and your SSH client updated. Software updates often include security fixes that patch vulnerabilities. If you're running an older version of SSH on a device, it might be susceptible to known weaknesses. For example, the list of supported MAC algorithms can be determined by options in `ssh_config` and `sshd_config`, and if these aren't updated, older, weaker algorithms might be used.
Regular updates help ensure that your SSH connections are using the latest and safest encryption methods. This applies to your router's firmware, your IoT device's operating system, and the SSH client on your computer. It's a bit like keeping your house in good repair; you fix the little things to prevent bigger problems down the line, so it's really worth doing.
Limit Access and Permissions
When you set up SSH on a device, make sure you only allow access from necessary accounts. Avoid using the "root" or "admin" account for daily SSH access if possible. Create a regular user account with limited permissions, and then use that for your SSH connections. You can always switch to a more powerful account once you're securely logged in, if needed. This reduces the potential damage if someone were to somehow gain access to that limited account.
Also, consider restricting SSH access to only specific IP addresses if your router allows it. If you only ever connect from your home network, you could configure the router to only accept SSH connections from IPs within that network. This adds another layer of protection, making it harder for someone outside your home to even try to connect. It's about being smart with who gets to talk to your devices, and how, you know.
Frequently Asked Questions About SSH for IoT and Routers
How do I enable SSH on my IoT device?
To enable SSH, you'll usually need to access your IoT device's settings, which might be through a mobile app, a web interface, or sometimes a physical button sequence. Look for options related to "Remote Access," "Security," or "Developer Settings." Once found, you can often just toggle an SSH switch to turn it on. It's usually a pretty straightforward process, apparently.
What are the security risks of using SSH on a router?
While SSH is secure, misconfiguring it can create risks. If you use weak passwords, don't update your router's firmware, or leave the default port open to the internet, you could be vulnerable. It's important to use strong, unique passwords or, even better, SSH keys, and to keep your router's software current to protect against known issues. That's really what it comes down to.
Can I access my smart home devices remotely using SSH?
Yes, you absolutely can access smart home devices remotely using SSH, provided they support it and you've set up port forwarding on your router. This lets you create a secure tunnel from outside your home network directly to your device. It's a great way to manage things securely when you're not physically there, which is pretty convenient.
Conclusion
Getting a handle on SSH for your IoT devices and router is a really smart move for keeping your connected home safe. It's about taking control of your device security, making sure your remote access is protected, and just generally feeling more confident about your digital setup. From setting up secure keys to handling those occasional connection hiccups, having a good grasp of SSH can help you manage your devices with peace of mind. It truly helps to know how to set up and troubleshoot these connections, like when your Git operations give you trouble, or you need to get to a database remotely. So, consider giving your connected life that extra layer of protection, you know?
To learn more about secure remote access on our site, and to get more tips on IoT device security, check out our other helpful guides. For deeper insights into network security, you might also want to visit the OWASP Top 10 project, which offers valuable information on common web application security risks.
Comprehensive Guide To SSH IoT Device Router Setup
Mastering SSH IoT Device Router Setup: A Comprehensive Guide
SSH into your IoT Enterprise Gateway - NCD.io